WORDTIMES 39.
WORDTIMES 39. THE NATURAL STUDY OF VACUUM |
|
|
This essential space is a special
modification of time. It is a curvature because it starts practically from
one point and because the wavespace of an atom almost reaches the Moon
within one second. Well, although this wave field does not bend, but
it is curved, it behaves optically. We do not need to prove this, this is
what all of the observations of the science of optics is all about. All
media through which light passes behaves optically. This is true of a
thick boiler plate, only we do not notice this, we cannot see this in
visible visible |
|
|
in case of a mirage |
The consequence of this is that in the Earth's increasingly thin atmospehric air layers of different excitation-levels, light significantly bends. It has many implications. The stars are almost never seen where they are in reality. This discrepancy gets stronger especially in the vicinity of the horizon, as light needs to pass through ever-thicker layers of air. This is pinnacleized in oru next example. |
|
In cases of special
stratification, the degree of light diffraction can be so much where such
a reflection phenomena occurs. This is called a mirage. |
 |
|
Why did I quote these centuries old observations and theories here? Because the thin - outer-space-thin - medium behaves in the same way. The Earth's atmosphere is 60 km thick, but at ten kilometers up air pressure is only a third. Spaceships flying a hundred kilometers high practically travel already in vacuum. The question is, in how many atoms'near and distant effect field, a light quantum flying "arrow-straight" passes until it has broken through Earth's atmosphere? Because, as we know, it also gets scattered, and that is why we see the sky to be blue- green. That is, atoms in the atmosphere absorb many light quanta and also release them after a while. But although light comes to them from one direction in the case of absorption, they scatter light in all directions. This emission spectrum carries the characteristic emissions of the main components. It is one part oxygen and four parts nitrogen. However, the setting (and rising) Sun is still seen red. |
|
|
There is no doubt that from the quite
homogeneously distributed sunlight passing through the thicker air layer
the higher frequency components begin to be filtered more and more so its
color is shifting towards red. |
Created by photographer Jolán Csontos |
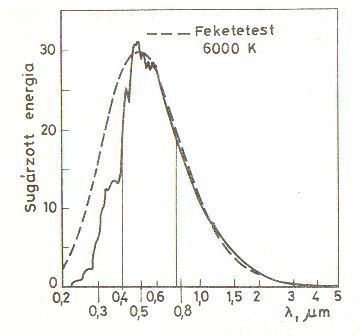 |
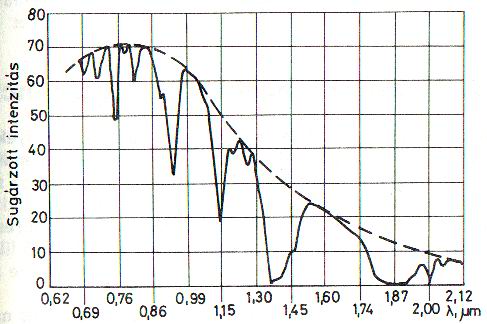
The picture shows the spectral radiation distribution of the Sun. The dotted line is the radiant curve of the black body, which would be the ideal distribution. This curve was extraterrestrial, that is, it was measured in space. The two parallel vertical lines is the visible band. This decade-long measurement still ignores a lot of things. But we can observe in it that there is almost no radiation at the 3 micrometer wavelength, and it is virtually eliminated at 5. Likewise, it disappears on the left at approx. 0.22 micrometers. It's now ultraviolet. This thing's good for Earth's dwellers, because harmful radiations, as a result of this beneficial color filtering will not reach the Earth. The main cause of this is the solar wind, the Sun's corpuscular radiation. Between the Sun and the Earth, there are atoms that fly towards Earth throughout 150 million kilometers. The Van-Allen belt provides additional protection which is kept alive by Earth's magnetic field. It's like a cushion embracing our planet. Interestingly, it carries a lot of nitrogen. |
|
By passing through the atmosphere, more and more shortages are beginning to emerge in this sloping distribution curve and it is mainly caused by water vapor in the air. It is visible in downward valleys. Likewise, all materials incorporate their signature in this starlight. In the same way, the cosmos filters light directed towards us. The light of each star (which differ in themselves also) is filtered by a filter whose thickness is distance- related and this is even further fleckered by local factors because the stars have different emanations. Similarly, the supernoves' particles flying apart are a strong filters and so are the interstellar nebulae. Emission lines show the original radiation, the adsorption ones show the absorbed spectrum, that is the signature of the substance through which it passed. |
The absorption spectrum of water. |
|
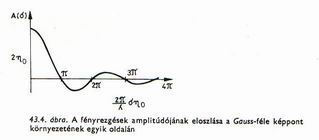
Gaussian distribution |
If we mirror this picture in our
imagination, then we get the Gaussian curve of the intensity distribution.
The light quantum passing near or far from the atom is more or less
diffracted. This phenomenon also exists at macro level, think only of the
measurements which have just recently been done. |
|
The readers - when our rhetoric
explores more familiar ranges-will get lively immediately. When this is so
the number of comments (and the virus attempts) goes up also. Our next
issue will be like this.
|
|
|
|
|
|
UNIVERSUM UNIVERSITAS 2003 September 23 ALL RIGHTS RESERVED ©
This publication was prepared for personal use only.
|
|
| |
|
 There is no
empty space. What we call outer space today is very thin but it is
not totally empty. A world-wide proof of this fact is that NASA is also
considering "sailing" spacecraft powered by sunshine. This is set into
motion by the effect of corpuscular radiation of the Sun and light
pressure. The former means all kinds atoms of small atomic weight, flying
radiallly in relation to the Sun, the latter is the light quanta. Of
course, the planets and their moons have evaporations. This includes even
comets, which also scatter many materials into their environment. It
is also important to note, that there is no compact material, i.e. the
atoms do not end at their electron shells but they have an endless
emanating field.
There is no
empty space. What we call outer space today is very thin but it is
not totally empty. A world-wide proof of this fact is that NASA is also
considering "sailing" spacecraft powered by sunshine. This is set into
motion by the effect of corpuscular radiation of the Sun and light
pressure. The former means all kinds atoms of small atomic weight, flying
radiallly in relation to the Sun, the latter is the light quanta. Of
course, the planets and their moons have evaporations. This includes even
comets, which also scatter many materials into their environment. It
is also important to note, that there is no compact material, i.e. the
atoms do not end at their electron shells but they have an endless
emanating field.